AI crawlers from OpenAI, Anthropic, and Perplexity now scan millions of websites daily, fundamentally changing how your content gets discovered and used. Most businesses struggle with whether to block these bots or welcome the additional traffic they can generate.
We at Emplibot see companies making hasty decisions without proper frameworks. This guide helps you create an AI crawler policy with robots.txt that aligns with your business goals.
What AI Crawlers Actually Do on Your Website
GPTBot from OpenAI, Claude-Web from Anthropic, PerplexityBot, and CCBot from Common Crawl represent the new generation of AI crawlers that operate differently from traditional search engine bots. While Googlebot indexes pages for search results, AI crawlers extract content to train language models or generate real-time answers for users.
Training Crawlers vs Answer Engine Bots
GPTBot scans websites to improve ChatGPT’s training data, consuming content without providing direct traffic returns. PerplexityBot crawls content to provide source citations in AI-powered search responses, creating potential referral opportunities. CCBot from Common Crawl creates massive datasets that multiple AI companies use for model training, making it one of the most aggressive crawlers currently active. These bots extract your content for fundamentally different purposes than traditional search indexing.
Traffic Returns Remain Minimal from Most AI Sources
Analytics data reveals that AI crawlers currently generate less than 1% of total referral traffic for most websites, according to recent webmaster reports. PerplexityBot provides the highest conversion potential among AI crawlers, as users who click through from Perplexity searches demonstrate 4.4 times higher engagement rates than traditional organic visitors.
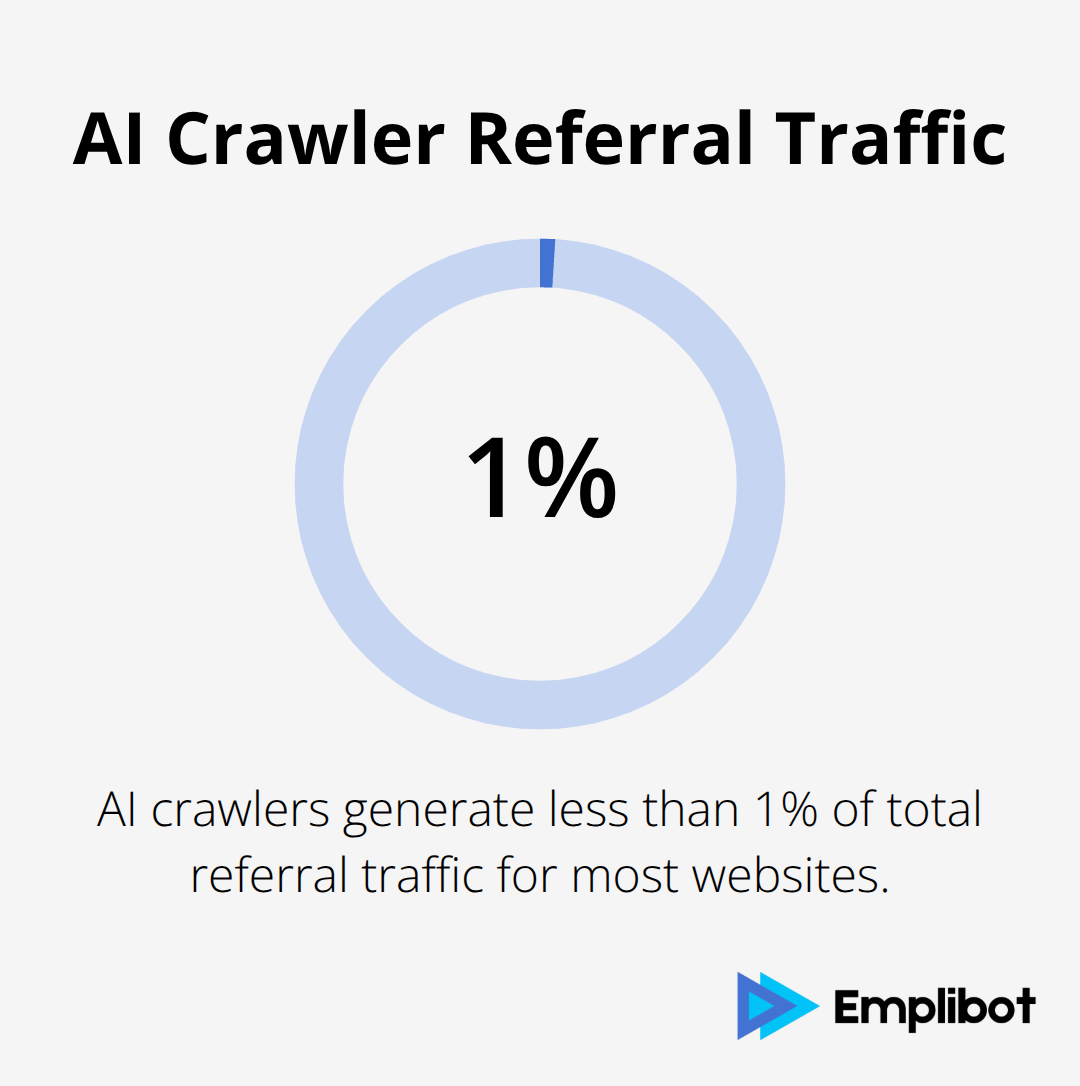
Training-focused crawlers like GPTBot and CCBot offer no direct traffic benefits since they only consume content without providing clickable references. ChatGPT’s 800 million weekly active users represent massive potential reach, but the platform rarely includes direct website links in responses (limiting immediate traffic gains).
Content Usage Rights Create New Legal Considerations
AI crawlers extract and repurpose website content in ways that traditional search engines never attempted. Training crawlers incorporate your text directly into AI model knowledge bases, while answer engines quote substantial portions of your content in user responses. AI companies must comply with copyright requirements and publish training data summaries under new regulations.
This regulatory shift means websites that currently allow AI crawling may gain recognition and potential compensation, while blocked sites lose influence over how AI systems represent their expertise. Your robots.txt decisions today will determine whether your content shapes tomorrow’s AI responses or gets excluded from this emerging traffic source.
How to Build Your AI Crawler Strategy
Your AI crawler policy requires three core decisions that determine whether these bots help or hurt your business growth. Most companies make these choices without proper analysis of their traffic patterns and business model requirements.
Content Protection vs Traffic Opportunity Trade-offs
Content-heavy businesses with proprietary research or competitive intelligence should block training crawlers like GPTBot and CCBot to prevent unauthorized use in AI model development. SaaS companies and service providers benefit from PerplexityBot and ChatGPT crawlers because AI-generated answers often include business citations that drive qualified traffic.
E-commerce sites see minimal value from AI crawlers since product recommendations rarely convert through AI platforms, which makes blocking the safer choice. Publishing companies face the biggest dilemma: blocking protects content ownership but eliminates potential reach to ChatGPT’s users who might never find their articles through traditional search.
Revenue Source Analysis Drives Bot Permissions
Companies that generate over 60% revenue from organic search traffic should allow answer engine crawlers like PerplexityBot because AI search visitors convert at higher rates than regular organic traffic. Lead generation businesses benefit most from AI crawler access since detailed service explanations in AI responses often include company mentions and contact information.
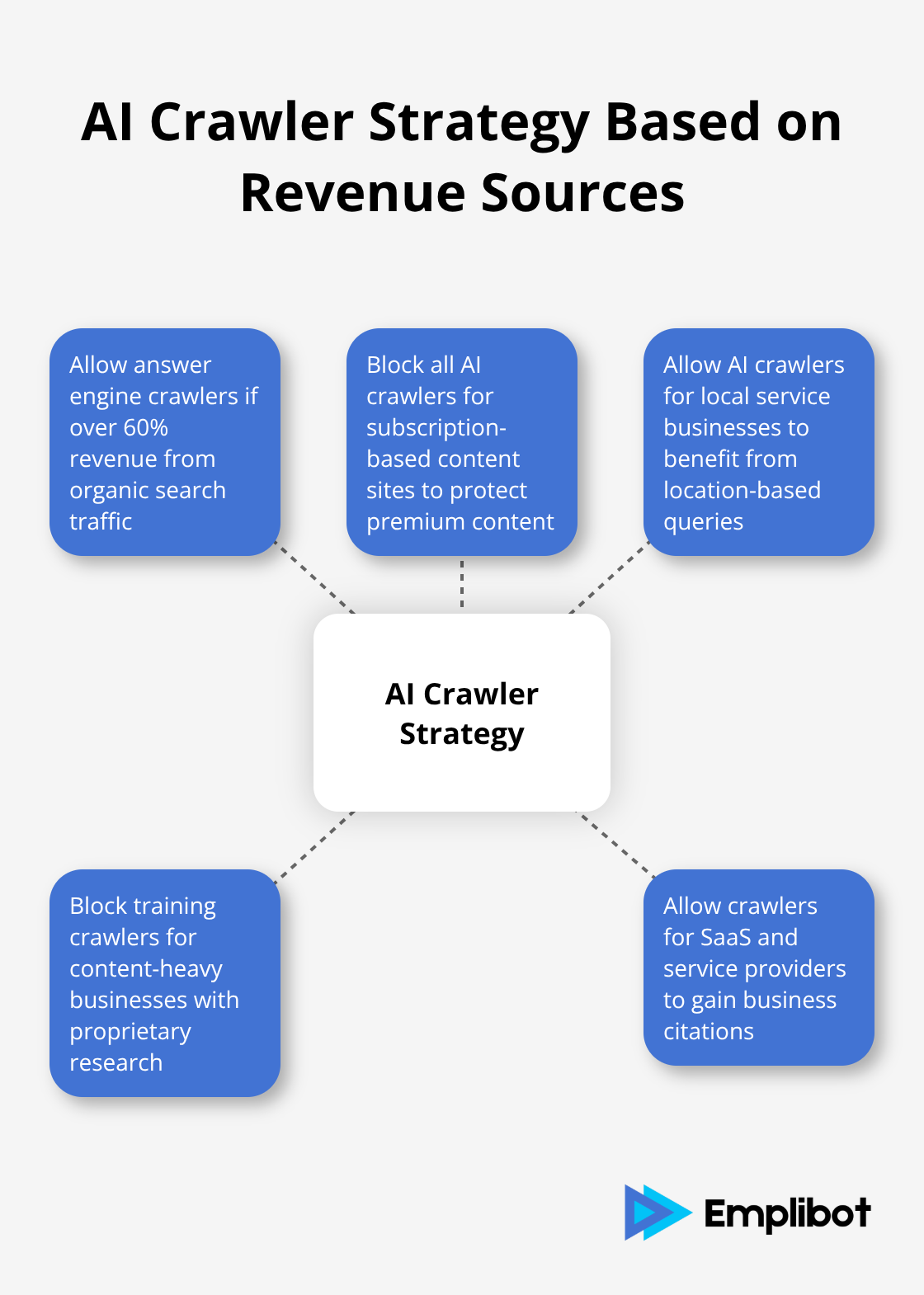
Subscription-based content sites should block all AI crawlers to protect premium content from free access through AI platforms. Local service businesses gain significant advantages from AI crawlers because location-based queries frequently trigger business citations in AI responses (creating new customer acquisition channels that traditional SEO cannot match).
Legal Posture Shapes Your Bot Strategy
Companies with strong intellectual property portfolios should document their AI crawler restrictions to establish clear legal boundaries for content usage. Businesses that rely on thought leadership and industry expertise benefit from selective crawler access because AI citations can establish authority and drive referral traffic.
Organizations subject to strict compliance requirements (like healthcare or finance) must evaluate whether AI training datasets could expose sensitive information through model outputs. Your legal team’s risk tolerance directly influences whether you allow training crawlers versus answer engine bots that provide attribution links.
The next step involves translating these strategic decisions into specific robots.txt rules that major AI crawlers will respect. Consider using SEO software to monitor how these policy changes affect your search visibility and backlink profile.
How to Configure robots.txt for AI Crawlers
Your robots.txt file controls AI crawler access through specific user-agent directives that target individual bots. Add these exact rules to your robots.txt file: User-agent: GPTBot followed by Disallow: / blocks OpenAI’s crawler completely, while User-agent: PerplexityBot with Allow: / permits Perplexity’s answer engine to access your content. For Common Crawl’s aggressive CCBot, use User-agent: CCBot and Disallow: / to prevent bulk data collection. Place these rules at the top of your robots.txt file before general crawl-delay settings to maximize compliance rates.
Exact Syntax for Major AI Crawlers
Configure your robots.txt with precise user-agent strings that AI companies recognize. OpenAI’s GPTBot requires “User-agent: GPTBot” followed by your access decision. Anthropic’s Claude crawler uses “User-agent: Claude-Web” as its identifier. Google’s AI training bot responds to “User-agent: Google-Extended” directives.
Perplexity operates multiple crawlers including “PerplexityBot” and “PerplexityBot-Preview” that need separate entries. Common Crawl’s CCBot ignores partial matches, so use the exact string “User-agent: CCBot” without variations. Meta’s AI crawler identifies as “FacebookBot” in robots.txt files.
IP and ASN Controls for Additional Protection
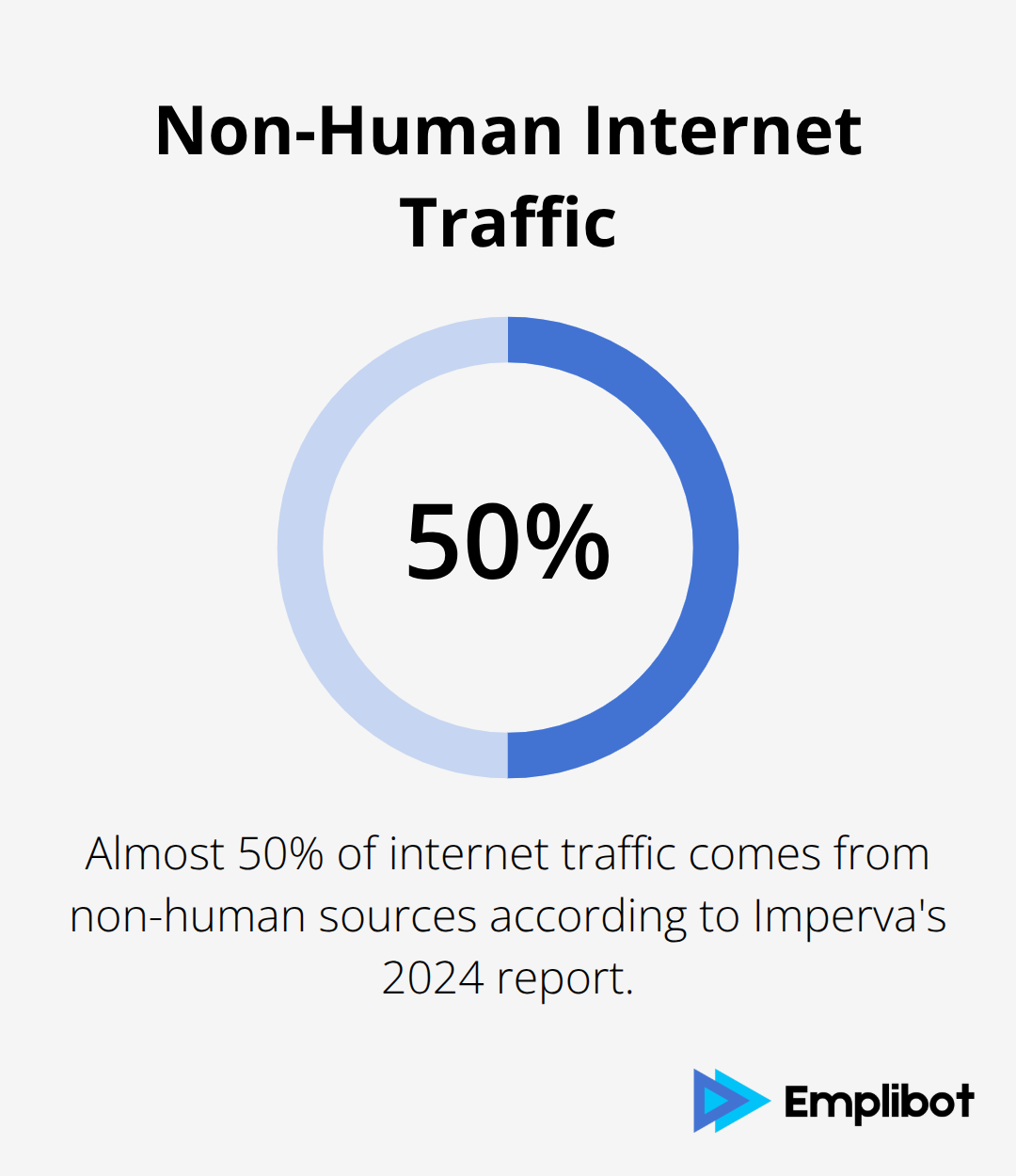
Robots.txt compliance remains voluntary, with almost 50% of internet traffic coming from non-human sources according to Imperva’s 2024 report. Supplement your robots.txt rules with IP-based controls through your CDN or firewall to achieve stronger enforcement. OpenAI’s GPTBot operates from ASN 20473, while Perplexity uses multiple ASNs including 13335.
Common Crawl distributes requests across residential proxy networks that make IP controls challenging. Configure your server to return HTTP 403 responses for blocked crawler IPs while maintaining robots.txt directives for compliant bots. Monitor your server logs weekly to identify new crawler IP ranges and adjust controls accordingly (as AI companies frequently rotate their infrastructure to maintain access).
Validation and Compliance Monitoring
Validate your robots.txt configuration with Google Search Console’s robots.txt tools or online validation tools that simulate crawler behavior across different user-agents. Check your server access logs for continued crawler activity after implementation – persistent requests from blocked user-agents indicate non-compliance that requires IP-level enforcement.
Most legitimate AI crawlers respect robots.txt directives within 24-48 hours of updates, while malicious scrapers ignore these restrictions entirely. Set up automated alerts for unusual traffic spikes from known AI crawler IP ranges to detect policy violations quickly. Test your restrictions monthly by temporarily allowing blocked crawlers and measuring traffic changes, then revert to your preferred settings based on conversion data and business impact analysis.
Final Thoughts
Most businesses should allow AI crawlers from established companies like OpenAI and Perplexity to capture additional traffic opportunities. The minimal current referral rates will likely increase as AI search adoption grows, making early access decisions strategically valuable. Companies that establish clear policies now position themselves better for future AI-driven traffic growth.
Create a simple AI crawler policy with robots.txt that documents your business goals, primary traffic sources, legal requirements, and citation preferences. Include specific user-agent rules for GPTBot, PerplexityBot, and CCBot based on whether each crawler aligns with your revenue model. Review this policy quarterly as AI platforms evolve and traffic patterns change.
Malicious scrapers ignore robots.txt directives entirely, so your restrictions only affect legitimate AI companies that respect these standards (pair robots.txt rules with IP controls for stronger enforcement when you protect sensitive content). The AI landscape will continue to shift rapidly, with new crawlers emerging and existing ones changing behavior. Emplibot can help automate your content strategy while you focus on optimizing these AI crawler relationships for maximum business impact.

